In the dynamic world of web development, React/Redux applications often find themselves in need of real – time functionality. Whether it’s powering a chat application or providing live updates on a dashboard, WebSockets emerge as a powerful tool. However, figuring out how to seamlessly incorporate WebSocket state and events into the React and Redux ecosystem can be a daunting task at first glance. Fear not, for in this exploration, we’ll uncover the secrets of using WebSockets within a Redux application, with Redux Middleware serving as our guiding light.
Understanding WebSockets
The WebSocket API is a revolutionary addition to the web development toolkit. Unlike traditional methods that rely on polling – continuously making API requests at set intervals – WebSockets enable a direct, bidirectional connection between a client and a server. This means instant communication, making it ideal for applications that require real – time data exchange.
Setting up the client – side connection is straightforward. With a simple new WebSocket(url) call, you initiate the connection. You can then listen for crucial events such as open, message, and close. For example:

To make the code more organized and reusable, creating a Socket class can be a game – changer. This class encapsulates the functionality of connecting, disconnecting, sending messages, and handling events.
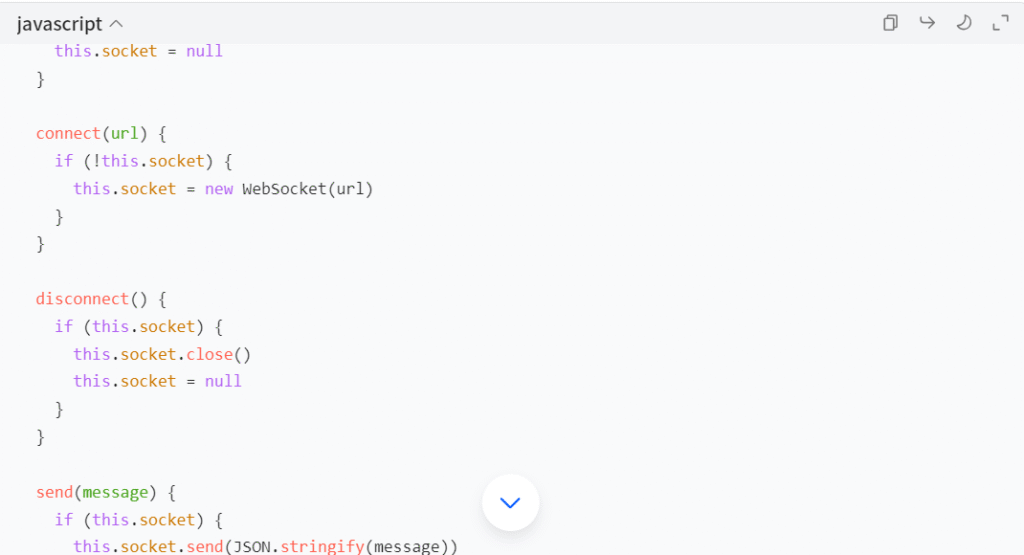
Using this class simplifies working with WebSockets, especially when dealing with multiple connections or more complex event handling scenarios.
The Role of Redux Middleware
Redux Middleware acts as a powerful intermediary in the Redux ecosystem. It allows you to intercept actions before they reach the reducer, giving you the ability to perform additional logic. In the context of WebSockets, middleware is the perfect place to manage the WebSocket connection and handle its events.
For our WebSocket integration, we’ll create a specific middleware. We’ll intercept socket/connect and socket/disconnect actions. When the socket/connect action is dispatched, we’ll open the WebSocket connection and set up event handlers. When the socket/disconnect action is triggered, we’ll close the connection.

Considerations and Future Explorations
This setup provides a solid foundation for integrating WebSockets into a Redux application. However, it’s important to note that with this approach, each browser tab will open a separate WebSocket connection. Whether this is the optimal strategy or if using the SharedWorker API and BroadcastChannel API for sharing connections across tabs is better remains an open question. In future articles, we’ll dive deeper into these alternative approaches, exploring how to create a more efficient and cohesive real – time experience in our Redux applications.
In conclusion, by leveraging Redux Middleware, we can effectively manage WebSocket connections within a Redux application, opening the door to a world of real – time functionality and enhanced user experiences.



